Enhanced Electron Transport in Heterojunction Sn-Perovskite Solar Cells Assisted by [6,6]-Phenyl-C61-butyric Acid Methyl Ester as a Dopant
Abstract
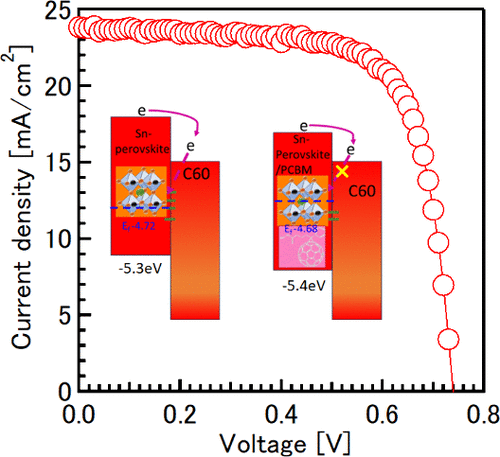
Tin halide perovskite (THP) possesses p-type semiconducting properties owing to innate Sn oxidative defect states. These defect states create imbalance in charge collection at the interfaces, which hinders overall solar cell efficiency. To effectively harness THP’s potential, we introduced a strategic n-type commonly used material, [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM), as a dopant, which has rarely been discussed. The coupling of PCBM and THP, validated through experimental and density functional theory methods, effectively targeted Sn defect states and transformed the THP semiconducting nature from p-type to intrinsic. Furthermore, strategically positioned PCBM at the grain boundaries offered multiple benefits, including improved adhesion between grains, leading to reduced lattice strain, enhanced energetic matching, and efficient charge transfer. This positing effectively harnessed electron collection due to PCBM’s n-type electronic properties, leading to an enhanced PCE. This blend strategy, broadly followed in organic solar cells, led to the development of PCBM-THP heterojunction solar cells, achieving a record efficiency of 12.68%.