Interfacial defect passivation and stress release by multifunctional KPF6 modification for planar perovskite solar cells with enhanced efficiency and stability
Abstract
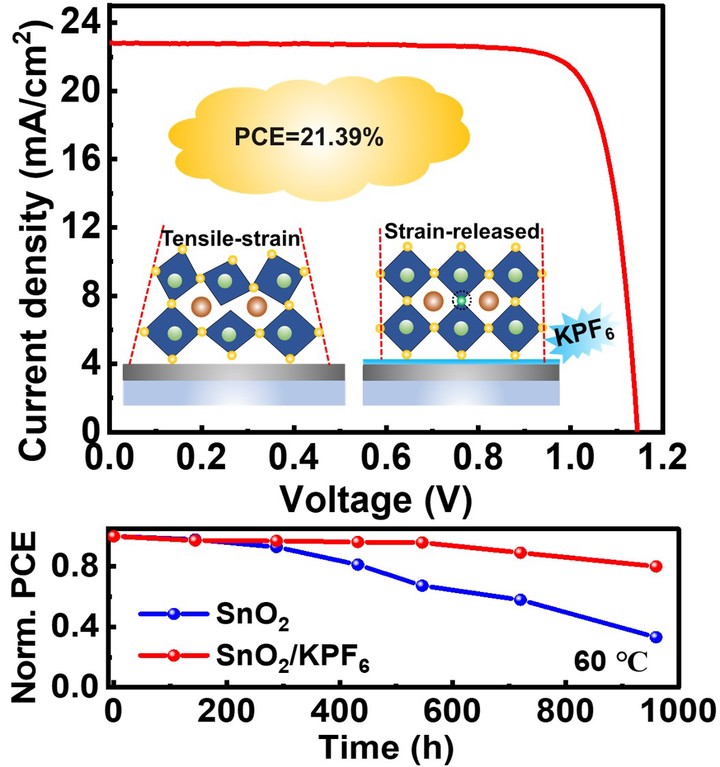
Interfacial defect and residual stress hinder the further enhancement of power conversion efficiency (PCE) and stability of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). Here, we report a multifunctional interface modification strategy where KPF6 molecule is employed to modify SnO2/perovskite interface. It is revealed that PF6− is still located at interface whereas most of K+ ions diffuse into perovskite layer. PF6− can chemically link SnO2 layer and perovskite layer via the hydrogen bond with perovskites and coordination bond with SnO2, resulting in improved interfacial contact. KPF6 interface modification leads to improved perovskite film quality, interfacial defect passivation, and interfacial stress release. As a result, the KPF6-modified device achieves an efficiency enhancement from 19.66% to 21.39% as compared to the control device. Meanwhile, moisture, thermal and light stability are ameliorated after interface modification. The unencapsulated KPF6-modified device maintains 80.1% of its initial PCE after aging for 960 h at 60 °C and 57.2% after aging for 960 h under one sun illumination, respectively. This work provides an idea for developing multifunctional interface molecules toward simultaneously enhancing efficiency and stability of PSCs.